What is SEO? The Easiest SEO Beginner’s Guide
The search term “What is SEO” receives about 49,500 queries in Google every month.
From SEO job seekers looking for a concise definition to use in a SEO job interview, and business owners trying to decide whether SEO is worth investing in for their businesses, to digital marketing beginners who just heard of the term and wanted to quickly look it up on Google, whatever category you belong, you are in luck!
This beginner guide you just stumbled upon is the easiest and most thorough SEO explanation on the internet.
So let’s get to it.
Table of Content
- What is SEO?
- Google algorithm: How search engines work
- Definition of basic terms
- Types of SEO
- SEO techniques
- Other forms of SEO
- How to do On-page SEO in 2019
- How to do Off-page SEO in 2019
- How to do Technical SEO in 2019
- How long does it take to achieve results in SEO?
- Peculiarities of Bing SEO
- Action point: SEO Practice Exercise
- How to assess your SEO results
What is SEO?
SEO is an acronym that stands for Search Engine Optimization, and it refers to the act of fine-tuning a website, web page, video or any piece of internet content for better visibility and ranking in the unpaid (or “organic”) results of search engines, especially Google, consequently increasing the traffic to the content.
To get a full understanding of how SEO works, you need to first understand the basic principles of how Google, Bing and the other search engines work.
Google algorithm: How search engines work
People visit search engines primarily to get answers, and they want those answers immediately.
In order to provide these answers instantaneously, search engines routinely send automated robots called crawlers to find, copy and store every new piece of internet content or web pages to their several servers around the world.
When you make a search on Google, it quickly scours all the previously saved internet content on it’s servers for relevant pages, and present the results to you, ranked in the order of popularity and relevance of the web pages to your search term.
Next question you may ask is, “how do search engines determine the relevance and popularity of a web page?”
They use complex mathematical equations called algorithms. The variables that make up these algorithms are what we routinely call search engine ranking factors.
Search engines are usually secretive about the exact factors that make up their algorithms, but, through countless experiments and live testing, SEO experts have been able to decipher the factors that influence rankings the most.
Google, for instance, is rumoured to have over 200 ranking factors. Of these, the 10 most important ones include: number and quality of backlinks, high-quality content, domain authority, mobile-friendly web design, dwell time, page speed, organic click-through rate (CTR), HTTPS implementation, social signals and structured data implementation.
An SEO professional, armed with the knowledge of these factors, continually fine-tunes client web pages for higher ranking on the search engines. We’ll look at each of these ranking factors in detail later.
Ranking factors are evolving
It is important to note that these ranking factors are as dynamic as the search engines themselves; they change over time. Whenever Google makes major changes to it’s algorithms, they release it under a new name (e.g. Penguin update, Panda update, etc).
At the turn of the century, you could get a web page to rank high in Google for a search term by using the search term and it’s variants excessively in the text, URL, and meta description of the page. This was called keyword stuffing.
But technological advancements, like machine learning, has helped search engines to become smarter in detecting such manipulations. Practicing keyword stuffing in 2020 will do your website SEO more harm than good.
Also, there are slight differences in the ranking factors of videos (on YouTube) as compared to web pages. Bing search engine has its own peculiaries too. We’ll look at these differences later in this guide.
Definition of basic terms
Keyword: this refers to the search term users enter into search engine to find your website; this is the term you are or should be trying to rank for.
Domain name: this refers to your website address, your URL.
Competitor: this word was borrowed from the business world, and it means websites or businesses currently ranking or trying to rank for the same keyword as you.
SEOs: this means search engine optimizers or search engine optimization experts.
SERP: this is an acronym for search engine results page; the page Google loads after a user enters a search term into it.
CTR: this is an acronym for click-through rate. It’s the number of clicks your website received in SERP divided by the number of times it appeared (impressions), multiplied by 100.
Types of SEO
When trying to rank a website in Google, there are primarily three types of SEO you need to know about:
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
- Technical SEO.
There are other types of SEO you may need to be aware about but some of them are not specific to ranking websites. They include Local SEO, Youtube SEO, E-commerce SEO, Linked SEO, Amazon SEO and App Store SEO. We’ll look at each one briefly later in this article.
On-page SEO is essentially about optimizing the actual content (text, images, etc) you are trying to rank in Google. It includes things like writing high quality content, keyword optimization, proper use of heading tags, title and meta description optimizations, etc.
The goal of On-page SEO is to present a content that Google will deem relevant to the search term the end user will type in the search engine.
Remember that websites are ranked on search engine result pages (SERPs) based on relevance and popularity.
On-page SEO activities are done on the website/webpage you are trying to rank, hence, the name “On-page”.
Off-page SEO, on the other hand, is about increasing a webpage’s reputation or popularity. The primary way Google and the other search engines judge a webpage’s popularity (or authority) is by the number of high-authority websites linking to the webpage.
Hence, Off-page SEO is all about trying to get other websites (especially those with high authority) to link to your content.
Off-page SEO activities are done outside the website/webpage you are trying to rank, hence, the name “Off-page”.
Off-page SEO activities include link outreach and guest blogging.
Technical SEO refers to activities such as improving site speed, mobile-friendliness, crawlability, implementing structured data, implementing AMP, etc. Essentially anything that can be done to better your website’s readability and user experience.
Some SEOs view technical SEO as a subset of on-page SEO.
SEO techniques
There are three categories of SEO techniques:
- Whitehat SEO
- Blackhat
- Greyhat SEO.
Whitehat SEO refers to any practice that improves a website’s search engine ranking ethically by adhering to Google Webmaster Guidelines.
Some examples of Whitehat SEO tactics encouraged by the guideline include using keyword research and optimization, internal linking, natural link building, use of alt tags in images and videos, proper usage of heading tags and title tags, writing unique high quality content primarily for users (not search engines), using a simple URL structure, mobile-friendly web design, improving page speed, use of SSL certificate, ensuring your website is crawlable for indexing, ensuring cross-browser compatibility, and implementing structured data.
Whitehat SEO tactics may be costlier and may produce results a little slower than Blackhat SEO but they are generally safer and better in the long run.
Blackhat SEO refers to attempts to improve a website’s ranking in ways that are deceptive and disapproved by search engines, with the hope of getting results quickly.
Examples of Blackhat SEO tactics discouraged in Google Webmaster Guidelines include keyword stuffing, creating thin and duplicate content, hidden texts and links, making pages with automatically generated content, automated backlink generation, and cloaking (the practice of presenting a content to human users that is different from what you presented to search engines).
All these tactics have been outlawed, and they can earn your website an SEO penalty. And even if they work, the results are short-lived and not sustainable.
Greyhat SEO refers to using questionable strategies that aren’t exactly banned by Google to obtain results in the short term. These strategies generally contradict the spirit of the Webmaster Guidelines but are not clearly spelt out in it.
Some examples of Greyhat SEO tactics include:
- Buying expired domains with good backlink profile, then repurposing them.
- Using Private Blog Networks (PBNs) with average content quality to build backlinks
- Link building using Web 2.0 submissions
- Boosting social signals by purchasing social shares and traffic
- Artificially increasing CTR by getting several friends across the world to Google your desired keyword and clink on your website multiple times a day.
Do Greyhat SEO tactics work?
Yes, they do. They can help rank a website higher and boost traffic in the short term but like Blackhat SEO, they are not good for business in the long run.
Here’s what Google has to say about Blackhat SEO on it’s Webmaster Guidelines page:
“These quality guidelines cover the most common forms of deceptive or manipulative behavior, but Google may respond negatively to other misleading practices not listed here. It’s not safe to assume that just because a specific deceptive technique isn’t included on this page, Google approves of it.”
That’s why those tactics are risky and not recommended.
Other forms of SEO
Local SEO
Ahrefs define Local SEO as the process of ‘optimizing’ your online presence to attract more business from relevant local searches on Google, Bing and the other search engines.
These days results in Google result page are of four parts: featured snippets (if available), the ads, local business listings (if applicable) and 10 webpages, depending on the search term the user enters into it.
For instance, when you search for “Learn Digital Marketing” on Google, you are probably looking for an informative article, a beginner’s guide, or some digital marketing course. So Google will present you a result page with 10 webpages (that they believe are popular and relevant to the search term) just below the ads.
However, if you search for “Digital Marketing Lagos”, Google assumes (and often rightly so) that you are looking for digital marketing agencies in Lagos, hence, they’ll list a number of such agencies in the result page, below the ads and above the 10 webpages.
So Local SEO is about positioning your business to show up among the local business listings when such location-based searches are made.
This Ahrefs guide by explains how to do Local SEO for your business.
YouTube SEO
Like Google, YouTube’s search engine has its own separate algorithm for ranking videos. The 10 biggest YouTube ranking factors are:
- Keywords
- Click through rate
- Watch time
- Video title
- Video description
- Video quality
- Tags
- Use of subtitles
- Overall view counts
- Number of comments, shares, like and subscriptions
This guide by The Offbeat Story explains YouTube SEO in further details.
LinkedIn SEO
LinkedIn has morphed from being a social network for professionals into a lead generation tool. It has a powerful search engine that can potentially produce the kind of lead generation results that your Local SEO efforts are currently doing.
LinkedIn SEO is essentially keyword research and infusing the keywords in various portions of your LinkedIn Profile. More detail on that here.
Amazon SEO
Like LinkedIn, Amazon.com has a search algorithm (called A9) that depends primarily on keywords. Amazon FBA merchants can use these steps to optimise their products for more traffic and sales.
App Store SEO
App Store SEO (ASO) is the process of optimizing mobile apps to rank higher in the store’s search result. The two most important app stores are Google Playstore and Apple iOs app store.
The following are the three important ranking factors for App Store SEO:
- Keyword-optimized App Title and description
- Total number of downloads
- User ratings/reviews.
Negative SEO
Negative SEO refers to the practice of using unethical blackhat techniques to decrease a competitor’s website rankings in search engine results.
Some Negative SEO techniques commonly used include:
- Directing numerous low-quality spammy backlinks to competitor’s website
- Redirecting Google-penalised domains to competitor’s website
- Backlinks with adult anchor texts (e.g. Viagra, Gambling, Porn Movie)
- Content scraping and duplication all over the internet
- Hacking a competitor’s website, changing it’s content and editing it’s robot.txt file (which can delete the website from Google).
Origin of Negative SEO
Negative SEO began to become popular in 2012 after Google released the Penguin update to it’s algorithm. Before this update, low-quality backlinks didn’t add or subtract from a website’s rank, Google just ignored them. But after the Penguin update, Google started to penalise websites that have acquired numerous low-quality backlinks unnaturally.
Bad-hearted SEO professionals took advantage of this loophole, and started directing thousands of bad backlinks at competitor’s website in an attempt to reduce their ranking and replace them on search engine result pages. This is the origin of Negative SEO.
To cushion this, Google released the Disavow Links tool on Search Console later that year, to help victims of Negative SEO curtail the effects of such backlinks.
Here’s is a video of Google’s Matt Cutts explaining why the Disavow Links tool was created:
Bing search engine also has a Disavow Links tool.
This guide on NeilPatel.com explains how to protect your website against Negative SEO attacks.
SEO in 2020: What works?
Now that we’ve seen the definition, types and various forms and techniques of SEO, it’s time we go into a little more details on the exact SEO tactics that work in 2020
How to do On-page SEO in 2020
Like I mentioned earlier, On-page SEO means fine-tuning the webpage you want to rank so that Google and users deem it relevant for the keyword you are trying to rank the webpage for.
The aim of on-page SEO is 3-fold:
- To convince Google that your content is relevant to the target keyword
- To entice users to click on your website (instead of others) on the SERP
- To make users stay longer on your website after clicking-through from Google, and engage with it by commenting or sharing it on social media.
These three aims should be the basis of all your on-page SEO efforts.
So here are seven (7) actionable on-page SEO steps you can implement today:
1. Write high quality content
You must have heard the phrase, “Content is King”. It’s a common cliche among SEOs.
But content is not only King, content is GOAT (Greatest Of All Time).
Literally!
If you could implement only one SEO lesson from this guide, this is it.
So what exactly is high quality content?
-
A high-quality content is keyword-optimized
You must always start the process of writing high-quality content with keyword research.
However beautiful, poetic or grammatically sound an article is, if it’s not deliberately written to target specific keywords, its SEO prospect is poor.
I’m always surprised every time I see creative writers publish beautifully crafted blog posts that don’t target any keywords.
I mean, what’s the point? Why waste quality time writing stuff no one will ever find online?
Such articles do not match user intent, hence, they have carry low SEO value.
Nobody will find your content through Google if it does not have specific keywords strategically placed in the title tag, meta description, h1 tag, h2 subheadings or the actual body of the article.
Ideally, your target keyword should appear within the first 100 words of your content.
Be careful not to overdo keyword optimization though, because Google penalises keyword stuffing.
The ideal keyword density recommended by most SEO experts is 1-3%.
Keyword density is the number of times your keyword appears in your content, compared to the total text of that page. So if you have a text that is 100 words and 3 of those are your focus keyword, your keyword density is 3%.
-
A high-quality content has LSI keywords strategically sprinkled all over
LSI is an acronym for Latent Semantic Indexing. LSI keywords are words that are related in meaning to your target keyword.
They could be synonyms of your keyword, or simply words that are frequently found together with your keyword because they share the same context.
For instance, if your content is about ‘Apple’. How does Google know you are writing about the maker of iPhones, not the fruit?
They check your content for Apple LSI keywords like ‘itunes’, ‘apple news’, ‘apple store’, ‘apple hulu’, ‘iphone’, ‘apple new ipad’, ‘apple stock price’ and ‘computers’. These words are frequently found in content written about the maker of iPhones.
Google uses LSI keywords, in addition to keyword density, to better understand the overall topic of your content, so that they can match searcher’s intent.
Now, a well written long blog post will naturally have LSI keywords, but for SEO sake, it’s beneficial to also deliberately sprinkle LSI keywords in your page in any of the following locations: title tag, h2 and h3 subheadings, meta description, alt-text of images, first paragraph of text, and internal link anchor texts.
Here’s a guide that explains how to find and use LSI keywords on your next SEO content.
-
A high-quality content is long enough
What is the ideal content length for SEO?
Long enough!
Backlinko analyzed 1 million Google search results in 2016, and found that the average word count of a Google first page result is 1,890 words.
SerpIQ conducted a similar study in 2012 involving more than 20,000 keywords, and the results showed that the average content length of each of the top 10 results was more than 2,000 words.
Because of these studies and other similar ones, SEOs generally believe longer content ranks better in Google, but in reality, that’s half-truth.
What really matters is that the content is long enough to thoroughly answer the searcher’s question (user intent again, you see?).
For instance, If I search for “Ikeja ZIP code”, I’m not looking for some 2,000 word definitive guide to ZIP codes. What I’m looking for is just a 6-digit number to use in filling out a form somewhere on the internet.
If instead I search for “Facebook ads beginner’s guide”, I’m definitely looking for a thorough and in-depth article.
So that the ideal SEO content length is niche-specific; it depends on the keyword you are trying to rank for.
Pro tip: Before writing any SEO content, always search for your keyword on Google, click through the top 3 results, and take note of their average content length (Use this free tool for that). Then set out to write longer, more thorough and more informative content than all of them.
-
A high-quality keyword is written to win featured snippets
Google started experimenting with featured snippets in 2013. Then, it was called “Quick Answer” boxes.
What is a featured snippet?
A featured snippets is a section of Google’s search result page that provides searchers with a concise and direct answer to their questions right there on the search results page, without the searcher having to click through to a specific result.
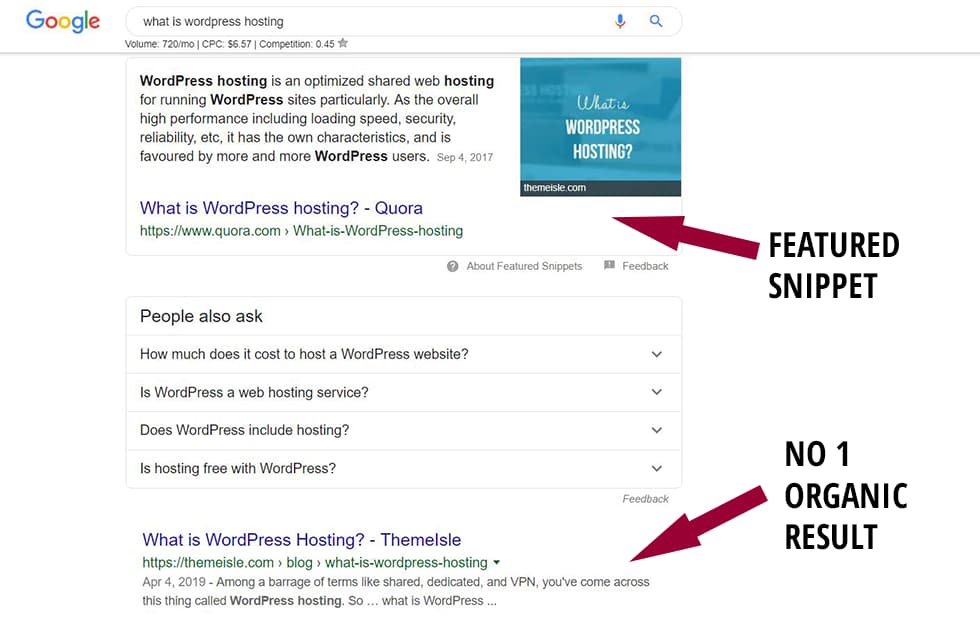
Featured snippets are seen more for keywords that ask questions, like how-to’s and what-is, and they are usually located at the top of the results page (above even the number 1 result). They come in 3 forms; a paragraph, a list or a table.
Why should you care about featured snippets?
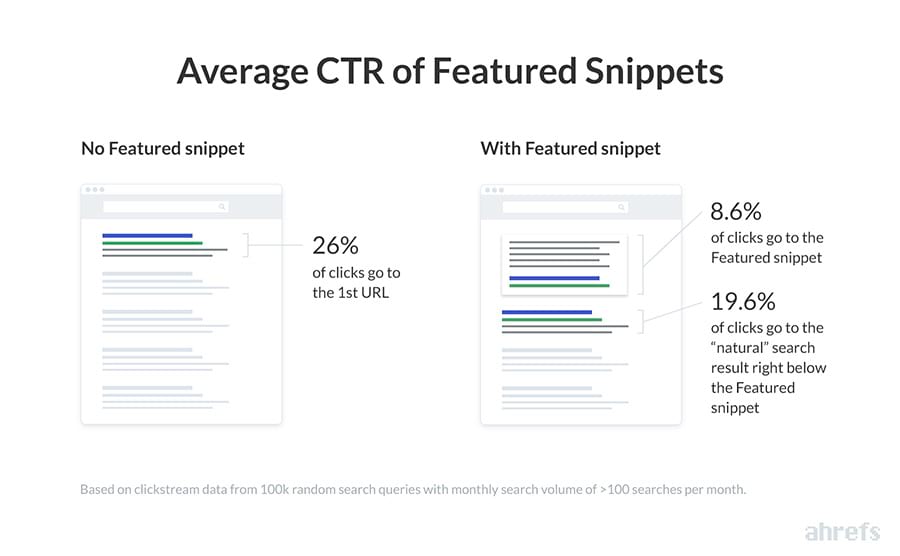
Because 12.3% of search queries have featured snippets in the search results. And a study of 2 million featured snippets by Ahref shows that featured results are already ‘stealing’ significant traffic from the top organic results.
Without a featured snippet, the first result gets a 26% click-through rate. With a featured snippet, the first result only gets a 19.6% click-through rate, and the featured snippet gets an 8.6% click-through rate.
So how do you win a featured snippet?
- Rank in page 1 of Google’s search result page. (99.6% of the featured snippets are from websites already in the top 10 positions in Google.)
- Use numbered or bullet lists and tables more often (and when appropriate) in your content.
Moz has a guide on how to win featured snippets. You should read it.
-
A high-quality content is rich in images and videos
Blog post with images are more interactive than long blocks of text. They tend to get more social shares, and consequently higher rankings.
This is supported by the Backlinko study of 1 million Google search result which found that content with at least one image significantly outperformed content without any images.

Nobody wants reads a long block of text; it’s boring.
Spice up your content by adding at least one image and/or video to your post, even if it’s a meme (like the one I just used).
-
A high-quality content is unique
Copying and pasting content from other websites will kill your website’s SEO. Even re-using a content previously published on your own website is seen as duplicate content by search engines.
Duplicate content confuses Google bots, so it’s bad for SEO. So avoid it.
Every single page on your website should have uniquely written and SEO-optimized content.
Even if your website is a news blog that will require that you sometimes quote people’s exact words which other news websites may also quote, make sure the editorial paragraphs before and after the quotes are unique and longer than the quotes.
2. Use short, descriptive and SEO-friendly URLs
Compare this URL:
https://blog.digitalyeast.com/category/cat-1/9878772.php
…with this:
https://www.digitalyeast.com/
…and this:
https://www.digitalyeast.com/
If you were looking for a guide on “creating WordPress child themes”, for instance, and the SERP has the three URLs above. Which will you click: the first, second or third?
The third, right?
Yes! But why?
Let me guess. Because the URL is descriptive and includes your search term! Hence, subconsciously, you believe the website is more likely to have the authentic information on creating WordPress child themes.
Hope you got the lesson?
Making your URL user friendly can increase your organic CTR (a very important ranking factor) and improve your SEO.
How to make user friendly SEO URLs?
- Always include your target keyword
- Avoid complex URL architecture, like this: https://www.digitalyeast.com/
blog/category/seo-news/what- is-seo - Keep the URL short but descriptive enough, like this: https://www.digitalyeast.com/what-is-seo
- Don’t include definite things like numbers and years in the URLs. This is so as to allow for updating the article later on.
Here’s a quick example below:
The URL for an article titled “Best 10 WordPress Real Estate Themes in 2020” should be this:
https://www.digitalyeast.com/
…and not this:
https://www.digitalyeast.com/
Why?
Because editing the article in the year 2021 or adding more items to the list will not be feasible if you use the latter URL.
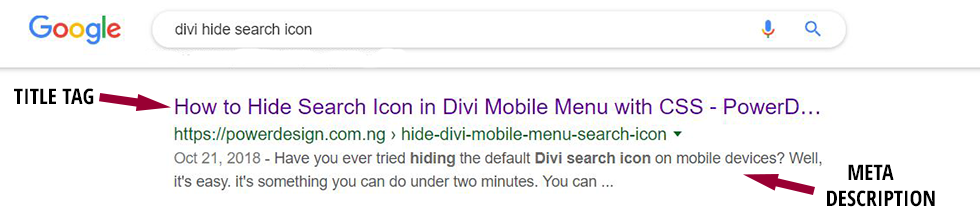
3. Optimize your title tag and meta description to entice user clicks
SERPs these days are crowded. You’ll see ads, featured snippets, local listings, ‘People Also Search For’ boxes, YouTube listings, images and 10 web pages.
Getting the attention of users is becoming increasingly difficult.
This is why you must entice them to click through to your website. Your title tag and meta description must stand out from the crowd; you must draw every click.
How do you achieve this?
- Always include your target keyword in the title, preferably at the beginning.
- Add adjectives like “best”, “top”, “easiest” or “2020” to the title.
- The title should be short, preferably 7-8 words.
- The meta description is an opportunity to pitch your content to the searcher in 155 characters; write your best pitch.
- Your meta description should also include your target keyword and a call to action.
4. Use h1 tags and h2-h6 subheadings appropriately
It’s good SEO practice to always wrap your webpage’s title in an h1 tag.
But what’s an h1 tag? What are h2-h6 subheadings?
Every webpage on the internet is written in HTML or some other programming language that outputs HTML. (HTML means Hyper Text Markup Language.)
Much like typing a document in Microsoft Office, HTML pages utilize headings for clarity and organization.
These headings are called heading tags or header tags. They are generally used to differentiate the headings (h1) and subheadings (h2-h6) of a page from the rest of the content.
They are also used to explain your content’s structure and hierarchy to the search engines.
The most important heading tag is the h1 tag and least important is the h6 tag.
Every web page should have a title tag, and at least one h1 tag in the content visible to the user.
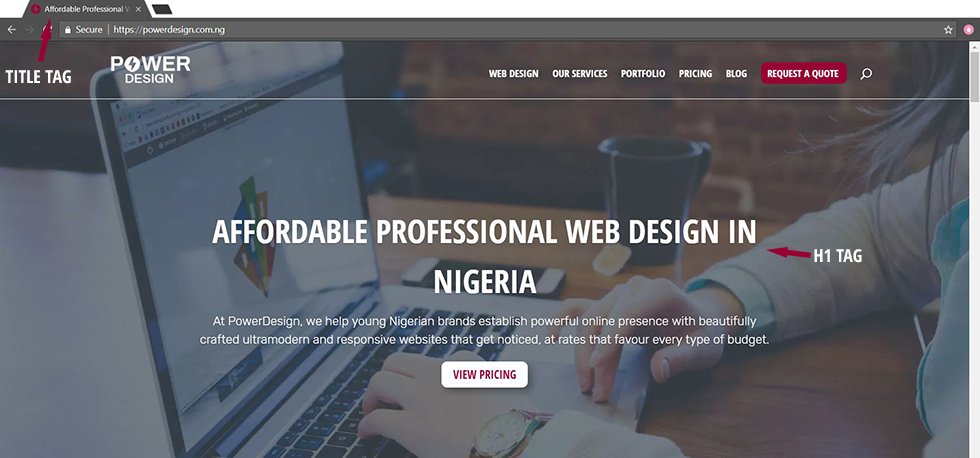
WordPress CMS automatically wraps the visible title of posts and pages in h1 tags, but you may still need to check your theme to confirm that it’s not configured differently.

When users first land on your content having clicked-through from Google, they skim through to see whether it’s worth their time or whether it solves their problems.
Then they may or may not read the whole thing. I bet you did the same when you opened this guide.
Google searchers don’t have time! They want answers to their questions and they want it immediately.
Where am I heading with us all this?
You must structure your website content to highlight the key points in the article, making it easier for users as they navigate through it.
One way to do that is the appropriate use of h2-h6 subheadings, numbered lists and bullets.
This guide by Alex Chris explains the use of heading tags for SEO in detail.
5. Optimize your images to rank
At least one image in your content should have an alt tag containing your target keyword. The other images too should have descriptive alt tags.
What’s an alt tag?
- It’s the text that shows when an image is hovered on your website.
- It’s the text that shows on the screen should an image fail to load.
- It’s the text that is read out to visually impaired people who may be accessing your website with a screen reader.
There’s a relationship between having keyword-rich descriptive alt tags and ranking in the top 10.
Also, your image file name should be descriptive. The featured image for this article, for instance, has the following file name and alt tag:
Alt tag: what is seo?
File name: what_is_seo.png
Here’s how to add an alt tag to an image WordPress:
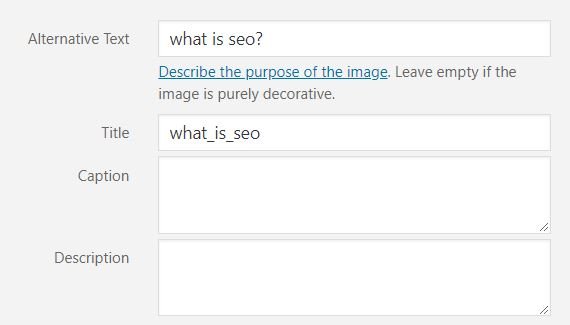
Lastly, all images in your content should be hosted on your domain/subdomain or at least should appear so.
6. Add external and internal links in your content
Linking to similar content on other people’s website is a way of proving to Google that your content is really about that topic.
Add at least 2-3 external links per 1000 words to your content.
Internal links serve the same purpose. In addition, they can help pass link juice from a successful SEO article to one less authoritative on your website.
You should use around 3-5 internal links in all your articles.
7. Improve user engagement
Google’s business model is based on satisfying searchers. They want to present the best content to visitors each time.
One of the ways they know whether your content is the best or most appropriate for a particular keyword is to actively measure how users interact with your website.
How?
They measure your content’s dwell time, social shares and blog comments.
Dwell time is the length of time a user stays on your website having clicked-though from Google, before hitting the back button to return to Google’s SERP.
When a searcher clicks the back button within seconds of visiting your page and continues searching on Google, it sends a signal to Google that your content is not appropriate for the keyword. So they’ll replace you or lower your rank on the SERP.
Dwell time is rumoured to be one of the top 10 Google ranking factors!
So, how do you increase your dwell time and reduce your bounce rate?
- Write high-quality content that is long enough.
- Write in simple, easy-to-read language, with short sentences and many paragraphs.
- Be amazing! Write content that is interesting to read.
- Flow. Always try to introduce your next paragraph in the last. That way, readers are glued in.
- Take advantage of multimedia. Add a bunch of helpful videos, infographics and charts to your content.
Social shares may not be a direct ranking factor but their ability to give your content an indirect SEO boost makes them a kind of big deal.
Try to encourage your users to share your article with their friends.
Articles that are controversial, funny or contain some new ground-breaking research and statistics tend to stimulate the highest number of social shares and user engagements.
Make sure it’s easy for readers to share your content on social media with just a click of the button.
If you are using WordPress, I recommend that you use this free plugin. It’s the best free WordPress social sharing plugin. We use it here on Digital Yeast.
A large number of high quality blog comments can also help your SEO. Always encourage your readers to comment on your content.
How to do Off-page SEO in 2020
Results are ranked on Google’s SERP based on their relevancy to the keyword and popularity of the website.
Off page SEO is all about increasing the popularity and authority of websites.
Link building
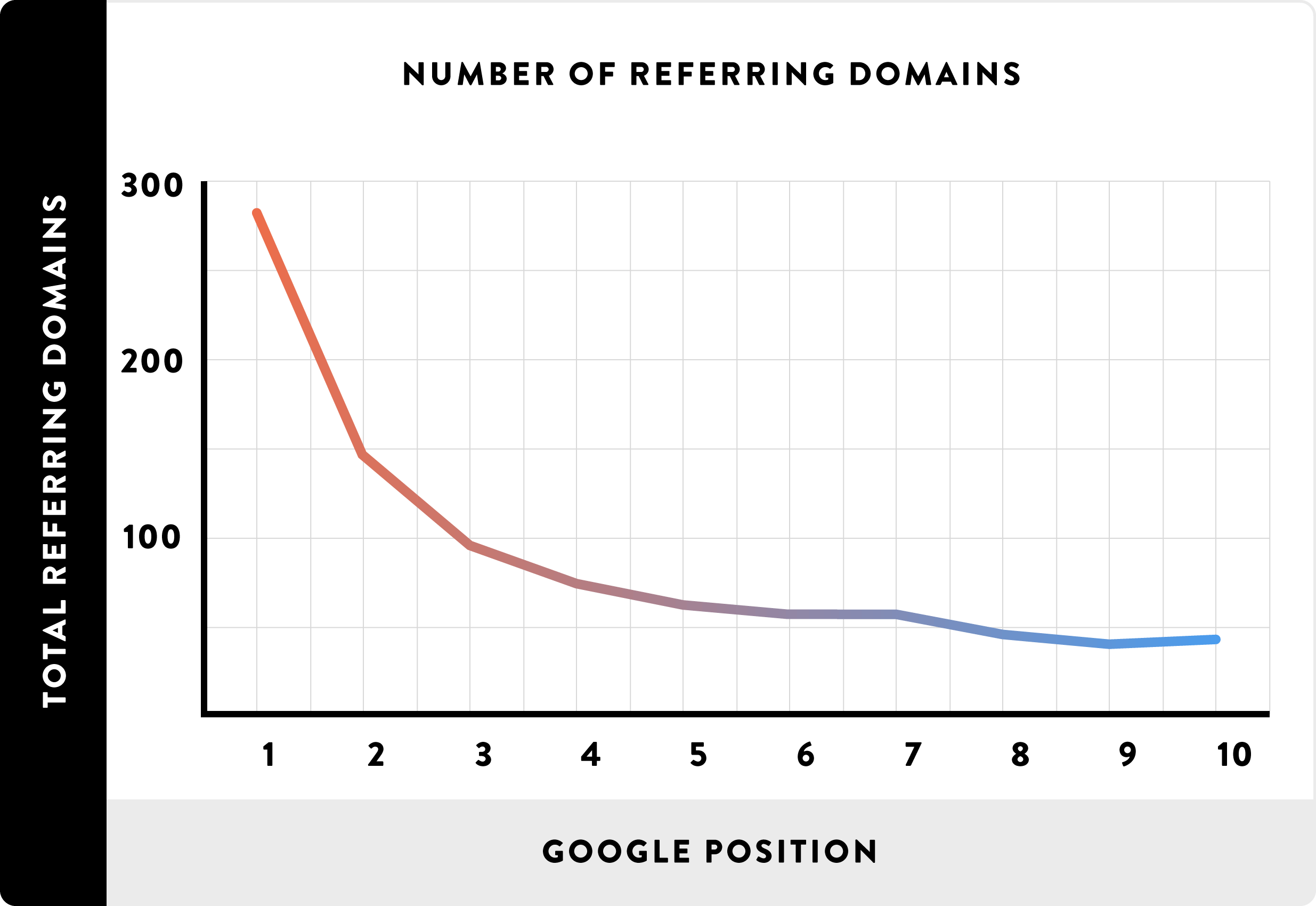
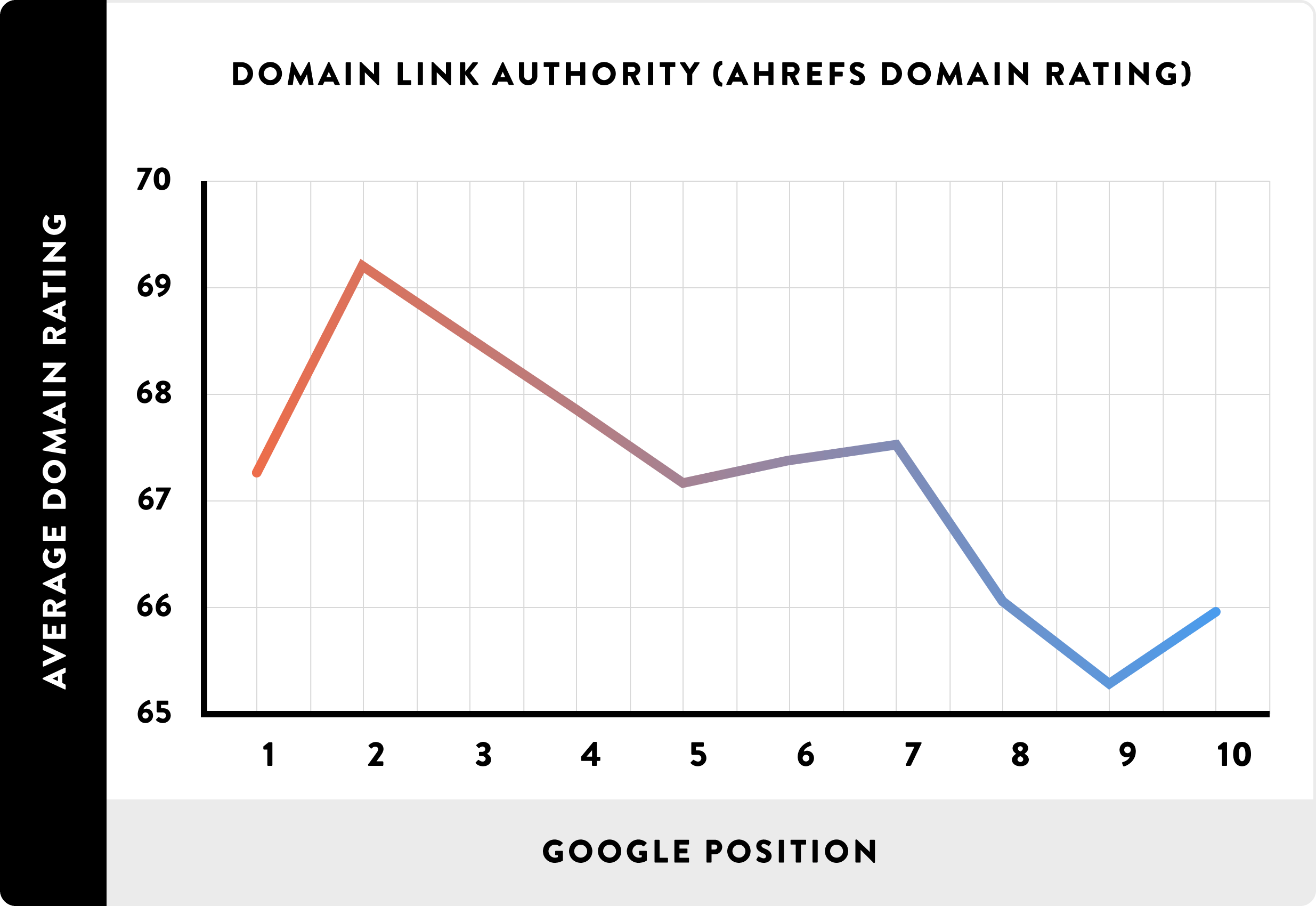
Like I mentioned earlier, the primary way that Google and the other search engines judge a webpage’s popularity (or authority) is by measuring the number of high-authority websites linking to the webpage. It’s been so since the late 1990s. And these links are called backlinks.
Generally, the higher the number of backlinks to an article, the higher the article ranks.
Also, the higher the authority of the websites linking to an article, the higher the article ranks.
Backlinko’s 2016 study of 1 million Google search shows a direct relationship between number of backlinks and higher search engine ranking. The study found that the number of domains linking to a page, as well as, the website’s overall link authority strongly correlates with higher rankings.
Higher authority websites can transmit their authority in a way to other websites they link to (especially if such links are dofollow backlinks). We call this “Link Juice”.
But all backlinks are not equal. In fact, certain kind of backlinks can hurt your SEO instead. Remember Negative SEO?
Nevertheless, number (and quality) of backlinks is the second most important Google search engine ranking factor, second only to high-quality content.
For such an important ranking factor, you’ll expect Google to publish a guideline explaining how to build quality backlinks to increase your website’s authority.
But take a look at what Google said about building backlinks in their webmaster guidelines:
Any links intended to manipulate PageRank or a site’s ranking in Google search results may be considered part of a link scheme and a violation of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. This includes any behavior that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site……The following are examples of link schemes which can negatively impact a site’s ranking in search results: buying or selling links that pass PageRank; excessive link exchange; large-scale article marketing or guest posting campaigns with keyword-rich anchor text links……The best way to get other sites to create high-quality, relevant links to yours is to create unique, relevant content that can naturally gain popularity in the Internet community……Creating good content pays off: Links are usually editorial votes given by choice, and the more useful content you have, the greater the chances someone else will find that content valuable to their readers and link to it.
Let me paraphrase it to you. Google is essentially saying that:
“We are aware of the fact that you know that backlinks influence search engine rankings but we don’t want you to put that knowledge to any use. Instead invest heavily in writing super high-quality content, then fold your hands, close your eyes, pray and hope that someone on the internet will miraculously find your content and link to it naturally.”
How does that sound to you?
Piece of trash, right? Yes!
Except your content is in a relatively new and largely untapped niche, writing high-quality content alone (without active link building) will not get your pages to rank on page one of Google.
Your competitors have probably actively sought out backlinks for their websites, and as such will continue to rank above you if you don’t do same.
Google even goes to the extent of discouraging guest posting for backlinks! Can you believe that?
What’s my recommendation?
Write unique high-quality content, ignore Google’s link scheme threats, and actively seek out new backlinks from high authority websites for your content.
But make sure the backlinks are from pages or websites that are topically related to your content.
Also, minimize the use of keyword-rich anchor texts in your guest posting efforts so that Google won’t begin to suspect foul play.
Joshua Hardwick, Ahrefs Head of Content, has put together an exhaustive guide where he shared 184 link building strategies. You can find it here.
Dofollow vs Nofollow Backlinks
Dofollow links tell search engine crawler bots to follow the link and they pass link juice to the page that was linked to.
Whereas Nofollow links tell search engine crawlers not to follow a link and they don’t pass link juice.
Ideally your website should have a healthy mix of both dofollow and nofollow backlinks.
Here’s what they look like in HTML:
Dofollow: <a href=”https://example.com”>I love Examples</a>
Nofollow: <a href=”https://example.com” rel=”nofollow”>I love Examples</a>
Certain CMS and page builders like WordPress make all links dofollow by default.
Brand signals
Off-page SEO is not only about link building. There’s significant evidence to show that Google uses brand signals as a ranking factor.
What are brand signals?
They are signals that show Google and users that your website represents a real brand (i.e., a real business, NGO, government agency, product, etc), and not just some generic blog created for SEO purposes only.
Search engines tend to favour websites of well-known brands in their result pages.
But how does Google distinguish real brands from just generic blogs?
Real brands have certain behaviours that Google can trace and measure. Some of these include:
- Real brands usually display clearly visible contact info, and their “About Us” pages are generally rich in information.
- They often have a physically accessible office address.
- They usually have people working for them, some of which are listed on LinkedIn.
- Real brands often have strong social media presence, with large following.
- Users often search for the names or products of real brands on Google. For example, “Mercedes Benz body parts”.
- Real brands are often mentioned on other websites without being linked to.
How to improve your brand signals:
- Create accounts on as many social media websites as possible and build your following on them.
- Become a guest contributor in popular websites in your niche.
- Sign up on as many review websites and business directories as possible, and get backlinks with branded anchor texts from them. Your priorities should be Yellow Pages, Google My Business, Bing Places, Yelp and Angie’s List.
- Get press coverage by being a source for a journalist on HARO.
- Run online visual ads without including a link to your website/product. If your copy or offer is enticing enough, users will search for your brand on Google.
- Invest in offline advertising. This too will increase the search volume for your brand name and improve your SEO.
How to do Technical SEO in 2020
Technical SEO is the part of On-page SEO that involves optimizing the technical aspects of a website.
The first goal of technical SEO is to improve user experience by making your website load fast, easy to read and easy to interact with.
The second is to make it easy for search engines to crawl, understand and index relevant content on your website.
Examples of Technical SEO activities include:
- improving site speed
- mobile-friendliness
- crawlability and indexiblity
- implementing structured data
- implementing AMP
- implementing canonical URLs and
- internationalization with hreflang tags.
Improving website speed
The first step to improving your website speed is to perform a pagespeed audit to know how fast or slow it currently is.
The following are some free pagespeed audit tools you can use:
These tools will show you how fast or slow your site is, then they’ll tell you what to do improve your site speed.
In general, you should target a page loading time of less than 3 seconds.
Here’s is how fast our website is:
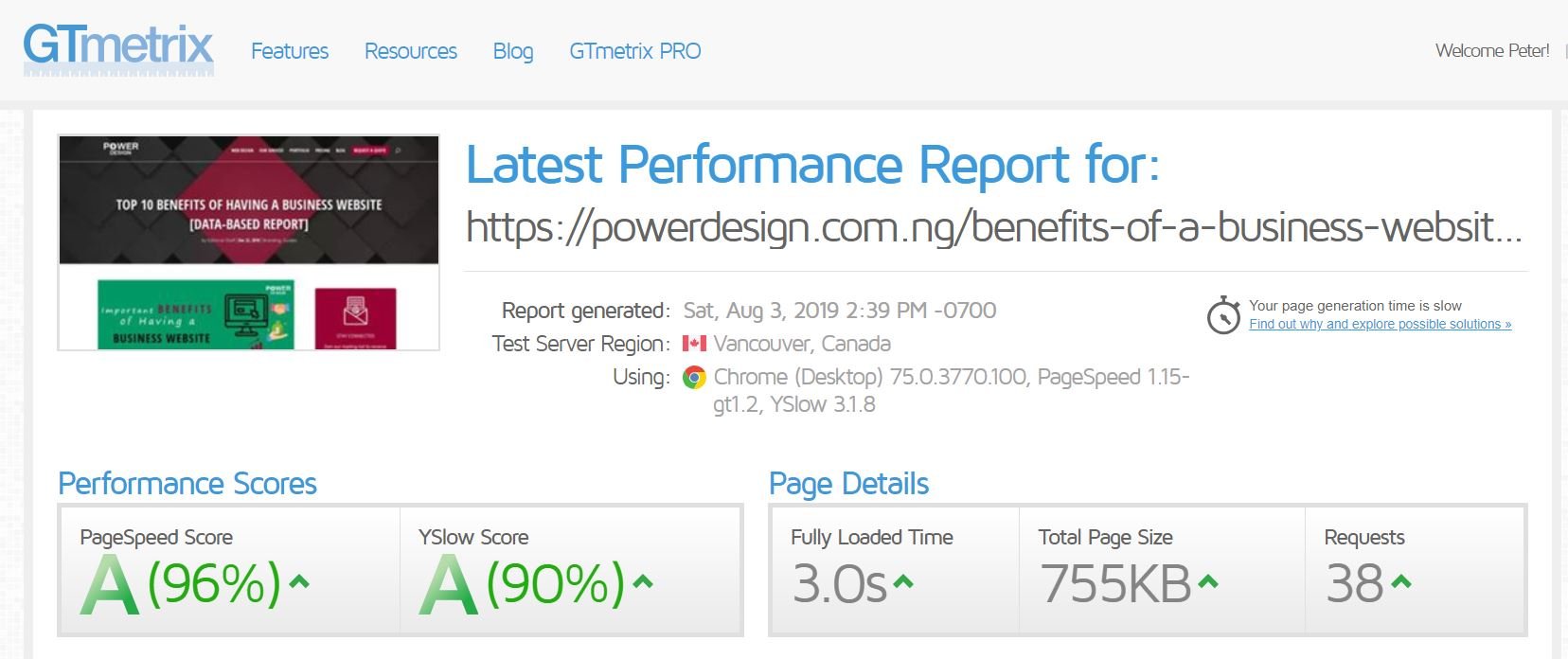
The factors that the determine how fast a web page loads include:
- The size (in KB or MB) of the page
- The number of HTTP requests
- How fast your web hosting server loads
- Whether web page is cached or not
- Whether CDN is used or not
- Whether the web page is static or dynamically generated.
This guide on CodeinWP explains how to speed up a WordPress website.
Mobile-friendly web design
In 2015, Google rolled out an algorithm update (Mobilegeddon) that prioritizes mobile friendly websites over those that are not. Having a website that displays well on smartphones and other mobile devices will help your SEO because according to a 2018 study, around 58% of website visitors use their phones.
Google also announced mobile-first indexing in 2018, which was officially rolled out on July 1, 2019.
What this means is that Google now predominantly use the mobile version of your web page for indexing and ranking.
If your website design is responsive, the content on both desktop and mobile versions will be the same, and there’s no need to fret.
There are three ways to implement a mobile friendly web design:
- Responsive web design
- Dynamic serving
- Separate URLs for mobile version

Google recommends responsive web design.
Responsive web design means that the HTML code of your website stays the same on both mobile, tablet and desktop devices, but the elements are styled with CSS so that the page adapts differently based on the device screen size.
All websites we craft at Digital Yeast are responsive by nature, they adjust and display well on all devices—mobile, tablet and desktop. Plus, they are extremely affordable. Get a quote here.
Recommended further reading on Technical SEO
- The Beginner’s Guide to Technical SEO by Quick Sprout
- Structured data with Schema.org: the ultimate guide by Yoast SEO
- How To Use WordPress Category & Tag Pages for SEO by Nate Shivar
- Google AMP: How to Implement it in WordPress by Kinsta
- rel=canonical: the ultimate guide to canonical URLs by Yoast SEO
- The Guide to International Website Expansion: Hreflang, ccTLDs, & More! by Moz.
How long does it take to achieve results in SEO?
Short answer: About 4-6 months.
Long answer: It depends!
The length of time it takes for SEO to work depends on a number of factors:
- The difficulty of your target keyword
- Your website’s overall backlink profile
- Whether you are targeting a global or local audience
- The age of your domain name
These four factors really are the most important determinants, assuming other factors such as quality content, page speed, responsive web design and HTTPS implementation are constant.
Certain keywords are supersaturated and almost impossible to ever compete and rank for.
For example, if you search for “how to create a website” on Google, you’ll notice that almost all the pages currently ranking in the top 10 are websites with very high domain authority (>90); some with thousands of backlinks.
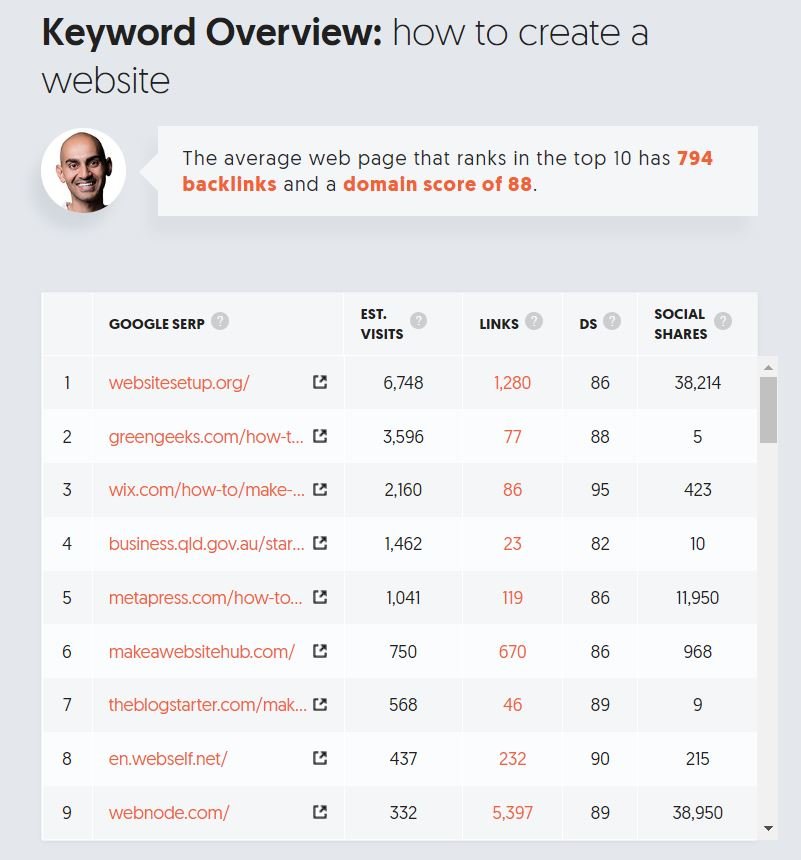
What this means is that in order to replace any of those websites currently ranking for the keyword, you’ll have to first write a super high-quality content that is much better and longer than all of them; then you’ll have to actively build quality backlinks to your content.
The minimum number of backlinks you’ll need is the number of backlinks of the webpage currently ranking number 10 (assuming that the number 10 result has the lowest number of backlinks on the first page).
Getting that number of backlinks ethically may take more than 1 year to achieve.
Sometimes, your article may have as much backlinks as the article ranking number one but still not be in the top 10 because your website’s overall backlink profile is too low.
That is, the total number and quality of backlinks pointing to your domain name (not just your article) is less than that of the websites currently ranking for your target keyword.
But if, for instance, you target a keyword that is in a niche that is still new and evolving, you may get a page 1 rank within 1-2 months, without any link building!
This is why SEO experts generally recommend that new websites should avoid saturated niches, and instead focus on finding keywords with low difficulty and moderate volume.
This guide by Spencer Haws explains in detail the process for finding low competition keywords.
One easy walk around this keyword difficulty problem is to target local audiences instead of global ones.
Ranking for “Web hosting in Nigeria” should be way easier than ranking for “Web hosting company”.
This is because the competition is less, but so also is the keyword volume.
Lastly, although Google has denied that domain age is a ranking factor, available evidence shows that domain age matters!
Building a blog on a domain name that is few years old is better for SEO than registering a new one.
Peculiarities of Bing SEO
Google owns 92.5% market share for search engines in 2019.
Bing.com is the world’s second largest search engine after Google (plus YouTube), with 2.5% market share.
Take a look the chart below:
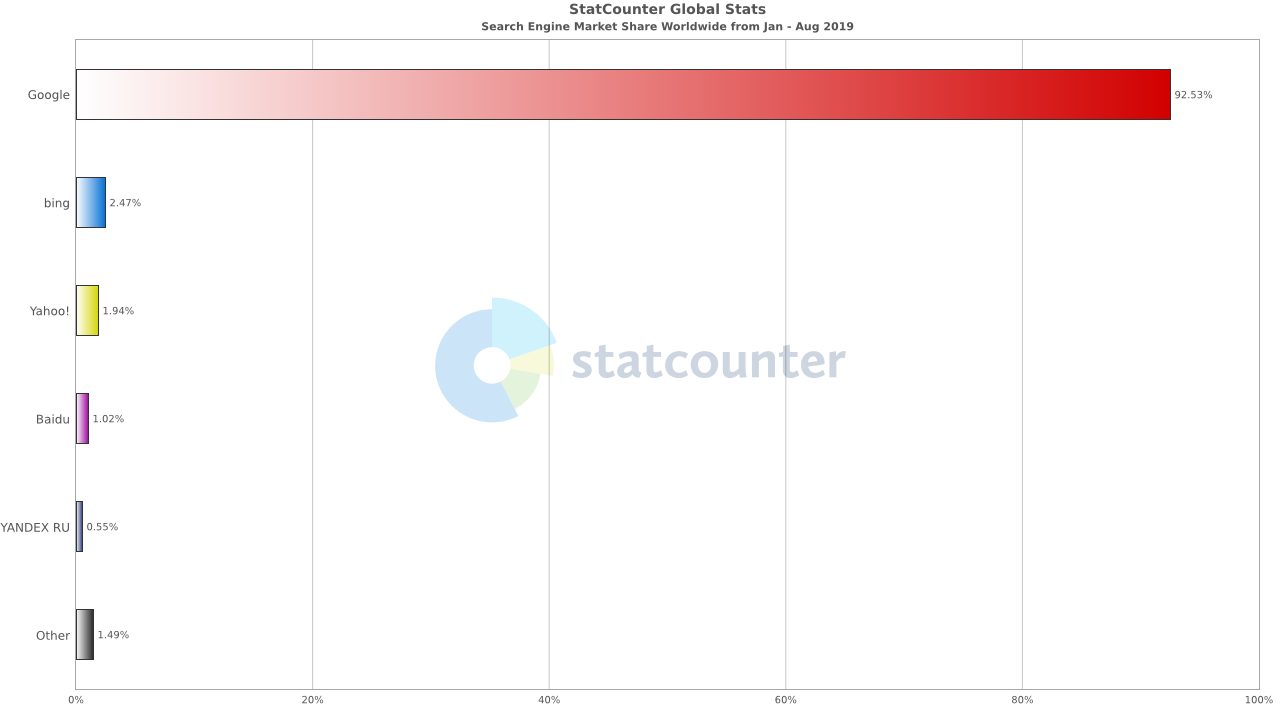
Bing’s 2.5% market share may seem small at first glance until you consider the fact that it approximates to roughly 12 billion searches per month. 12 billion!
Though good Google SEO would sometimes suffice for Bing too, it is worth mentioning that there are some subtle differences between Google SEO and Bing SEO.
Here are some peculiarities of Bing SEO:
Bing relies more on exact match keywords to understand your page’s context
Unlike Google that is able to understand and use the contextual meaning of a page to determine it’s relevance to a search query, Bing depends largely on the presence of exact match keywords in your page’s content.
They even recommended in their Webmaster Guidelines that publishers “use the keyword/phrase you are targeting a few times; use variations as well.”
So optimizing for Bing means you should consider using exact match domains; then add your target keyword and its variants in your meta description, meta keywords, title tag, h1 and h2 heading tags.
Keyword-rich anchor texts for links is good for Bing SEO
Still on the matter of keywords, Bing uses the anchor text of links (whether internal or external links) to understand the context of the page being linked to.
So much so that they recommend, in their webmaster guidelines, that publishers “use targeted keywords wherever possible”.
Here’s another line from the guidelines concerning internal linking:
Bing: Use targeted keywords as the linked text (anchor text) to support other internal pages.
But you’ll notice that I suggested earlier that you minimize the use of keyword-rich anchor texts while guest-posting for backlinks in order to avoid spoofing Google.
The trick, in optimizing for both Bing and Google, is to have a healthy mix of keyword-rich anchor texts and non-keyword anchor texts. And the keyword-rich anchor texts should be on the backlinks gotten from websites with high domain authority.
Bing recommends active link building
Unlike Google, Bing encourages active link building so long as it’s from related content and the links are not purchased:
Bing: Consider social media to help build external links, or simply ask websites for them; paying for links is risky.
Be careful though; generating a high number of dofollow backlinks suddenly within the space of one month to a content that probably had no backlinks before may trigger a red flag.
SEO experts recommend building no more that 20 links per month. This is called link velocity — the rate at which others are linking to your site.
Also, try focusing on quality instead of quantity.
Social signals matter
Unlike Google, Bing stated categorically that having huge number of engaged followers on social media that regularly share your content is a positive SEO signal.
Bing: Social media plays a role in today’s effort to rank well in search results. The most obvious part it plays is via influence. If you are influential socially, this leads to your followers sharing your information widely, which in turn results in Bing seeing these positive signals. These positive signals can have an impact on how you rank organically in the long run.
Free advertising credits and SEO tools
Like Google, Bing has robust Webmaster Tools with virtually all the features of Google Search Console such as sitemap submission, single URL submission, single URL removal, disavow links, inbound links tool, website geotargeting, mobile friendliness tool, etc.
They even have an SEO analyser that you can use to perform an SEO audit, then implement their suggestions.
One more thing; Bing gives publishers free $100 advertising credits when they sign up for Webmaster Tools.
However, this offer is limited to the following countries only: Argentina, Australia, Austria, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, France, Germany, India, Italy, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Peru, Spain, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States, and Venezuela.
Essentially, Bing loves publishers and are more transparent than Google.
Action point: SEO Practice Exercise
Now that you’ve learned the basics of SEO, what next?
Knowledge is useless if not applied. I suggest you put this knowledge to use immediately by starting a blog—an SEO optimised blog based on keyword research.
Not just some personal blog where you share your life experiences. If you are not a celebrity, no one will ever search for your life experiences on google.
The blog must not even be in a niche you are passionate or knowledgeable about. Just quality content based on keyword research.
Here are nine (9) steps to follow:
1. Do keyword research, and write down a list of 10 niches you can blog about
Use this free SEO tool for your keyword research, Ubersuggest. Make sure all the keywords you plan on targeting are within one niche. For example, “Woocommerce online store creation“, “Create WordPress blog“, “Create Shopify store“, “Choosing the right domain name“, “How to create a website with Wix” are all keywords within the Website Design niche.
2. Sort these niches by average keyword difficulty and monthly search volume; pick the best three
Choose the top three niches with the lowest average keyword difficulty and moderate to high monthly search volume.
3. Register three new domain names; or preferably buy good expired domains
If you opt for registering new ones, make sure they are exact match domains for your main target keywords or niche.
Choose a .com domain name if you are targeting a global audience, and a ccTLD (like .ng, .uk or .ca) if you are targeting a specific country.
I recommend targeting a global audience with two of the blogs and a local audience with the third blog.
4. Get simple logos designed for each domain name, and build superfast WordPress blogs on each of them
Delete all default WordPress posts, default pages and other thin pages. Uninstall all unnecessary plugins.
Make sure to install Yoast SEO plugin on each of the blogs, and noindex category pages, tag pages and other archive pages.
We can build these superfast WordPress blogs for you here at Digital Yeast for just £200 per blog. This special offer includes free logo design, free HTTPS implementation, domain name registration for 1 year and web hosting for 1 year.
5. Write 45 high-quality keyword-optimised articles; 15 per blog, each above 1,000 words
You can either write all the articles yourself or outsource them. Our content writers here can write them for you at just $60 per 1000 words. Send us a message.
On each blog, publish only 8 of the 15 articles; schedule the remaining 7 to be automatically published weekly for the next 7 weeks.
6. Create an account for each of the three blogs on Google Analytics, Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools
Then integrate the accounts with your blog, and submit a sitemap for each blog on Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
You’ll need these tools to assess your SEO results later.
7. Register each blog as a business on as many social media and business listing websites as you can
Make sure your profile description is the same on all of them, and try to get backlinks from them (whether dofollow or nofollow).
8. Actively promote and build backlinks from relevant sites to each of your blogs
Study this Joshua Hardwick’s exhaustive guide and implement some of the link building strategies he shared.
9. Wait for 4-6 months; then assess your result
Most of the steps above from keyword research to logo design, website creation, content writing and webmaster tools integration can be completed within one month.
The remaining 3-5 months should be spent actively promoting and building backlinks to your blogs.
During this period, avoid temptation to keep tweaking things on your blogs. Leave them as they are; wait for 3-5 months, assess your results, before implementing any further on-page SEO changes.
Avoid implementing every new thing you see in SEO videos on YouTube during this period.
Even after the 4-6 months waiting period, only make 1-2 on-page SEO changes per month. This is so that you can assess the impact of each change.
How to assess your SEO results
The following are the parameters to look at when assessing the result of your SEO campaign:
- Organic pageviews per month
- Percentage increase in organic pageviews per month in the last 6 months
- Number of impressions per month, organic CTR and bounce rate
- Number of keywords for which you rank in the top 10 results
- What percent of your 15 articles rank in the first page for their target keywords
- Number of featured snippets you’ve won
- Number of dofollow and nofollow backlinks you’ve acquired in the last 6 months
- Volume of searches for your brand name per month
All of these parameters can be assessed within Google Analytics, Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools without any need to use paid SEO tools.
I want to know about your result, you can send me a DM on Twitter if you’ve done this SEO practice exercise.
Also, feel free to ask any questions concerning SEO using the comment box. I’ll try to answer them.
A lot of effort went into creating this 8,500+ words guide. If you’ve learned something from it, I’ll really appreciate you sharing it with your friends using the social buttons below. Thanks
Related Posts
2 Comments
Submit a Comment

Digital Yeast is a leading web development agency, with 5 years experience helping young brands and small businesses establish powerful online presence with beautifully-crafted, fast-loading, ultramodern and responsive websites that gets noticed.
CONTACT INFORMATION
Address: Lokoja, Nigeria; Bradford, England.
support@digitalyeast.com
Quick Links





Thanks for the post. It will be the most definite guide for beginners to learn SEO & make a career
Thanks Yathav. Glad you found it helpful.